Theory of value (economics)
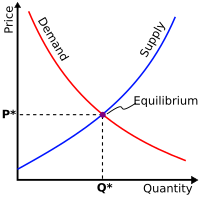
In economics, the theory of value means that the things that people want are worth something. It means people are willing to trade something that they have for something else that they value. For example, if you have a toy car and someone else has a toy airplane, you can trade your toy car for the airplane. Both of you have something that you value, so it makes sense to make a trade. The same idea applies to money; people are willing to trade goods and services for money because money can be used to buy other things that people want.
Related topics others have asked about:
