Channel length modulation
Okay, kiddo, let me tell you about channel length modulation. So, imagine you have a toy car with a driver in it. The driver can go faster if they press the pedal more, right? But what if the car gets bigger as the driver goes faster? That's kind of like what happens in a special type of electronic device called a transistor.
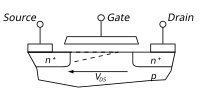
A transistor is a small device that lets us control the flow of electricity in a circuit. Inside a transistor, there are different parts called the source, drain, and gate. Think of them like the start, finish line, and a traffic cop directing the cars.
Now, the channel length is the distance between the source and the drain in the transistor. When we apply a voltage to the gate, it controls the flow of electricity between the source and the drain.
But, here's the thing – when the voltage between the source and drain increases, the distance between them starts to get smaller. Just like our toy car getting bigger, the channel length modulation causes the channel to narrow as we increase the voltage.
This can cause some problems because the transistor might not work as well when the channel gets too small. It could cause the current to flow more easily and make the transistor overheat or burn out.
So, scientists and engineers have to be really careful when they design transistors to make sure they take channel length modulation into account. They might use special materials or design tricks to help minimize the effect and make sure the transistor works the way it's supposed to.
And that's basically what channel length modulation is, buddy!
A transistor is a small device that lets us control the flow of electricity in a circuit. Inside a transistor, there are different parts called the source, drain, and gate. Think of them like the start, finish line, and a traffic cop directing the cars.
Now, the channel length is the distance between the source and the drain in the transistor. When we apply a voltage to the gate, it controls the flow of electricity between the source and the drain.
But, here's the thing – when the voltage between the source and drain increases, the distance between them starts to get smaller. Just like our toy car getting bigger, the channel length modulation causes the channel to narrow as we increase the voltage.
This can cause some problems because the transistor might not work as well when the channel gets too small. It could cause the current to flow more easily and make the transistor overheat or burn out.
So, scientists and engineers have to be really careful when they design transistors to make sure they take channel length modulation into account. They might use special materials or design tricks to help minimize the effect and make sure the transistor works the way it's supposed to.
And that's basically what channel length modulation is, buddy!
Related topics others have asked about:
