Global cooling
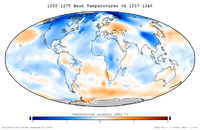
Global cooling is when the temperature of the Earth's climate decreases over a period of time. It can take place over many years, decades, or centuries.
Global cooling happens when there are too many particles in the air that reflect the sun's heat back into space, rather than it heating up the Earth. These particles, called aerosols, are created by natural sources, like volcanoes, and also by human activities, like burning coal and other fuels. The aerosols absorb energy from the sun, bounce it back into space, and cool the planet.
Global cooling happens when there are too many particles in the air that reflect the sun's heat back into space, rather than it heating up the Earth. These particles, called aerosols, are created by natural sources, like volcanoes, and also by human activities, like burning coal and other fuels. The aerosols absorb energy from the sun, bounce it back into space, and cool the planet.
Related topics others have asked about:
