Ionic bonding
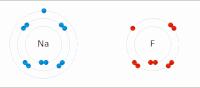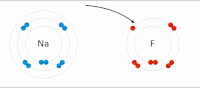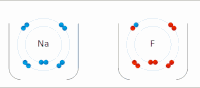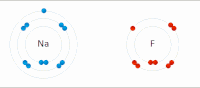
Imagine you have two magnets. One magnet has a negative force and the other magnet has a positive force. When you bring the two magnets close together, they stick together because opposite forces attract each other. This is similar to what happens when ionic bonding occurs.
In chemistry, atoms have a positive nucleus and negative electrons orbiting around it. Some atoms, like sodium (Na), have a positive charge and others, like chlorine (Cl), have a negative charge. When a sodium and a chlorine atom come close together, they are attracted to each other because opposite charges attract. The positively charged sodium atom loses one of its electrons and becomes a positive ion, while the negatively charged chlorine atom gains the electron and becomes a negative ion.
These two ions, now with opposite charges, stick together because they are attracted to each other, similar to the way the magnets stick together. This creates a compound called sodium chloride (NaCl), or table salt.
In conclusion, ionic bonding is the process where atoms with opposite charges stick together to create compounds like salt. It's like the way magnets stick together when opposite forces attract.
In chemistry, atoms have a positive nucleus and negative electrons orbiting around it. Some atoms, like sodium (Na), have a positive charge and others, like chlorine (Cl), have a negative charge. When a sodium and a chlorine atom come close together, they are attracted to each other because opposite charges attract. The positively charged sodium atom loses one of its electrons and becomes a positive ion, while the negatively charged chlorine atom gains the electron and becomes a negative ion.
These two ions, now with opposite charges, stick together because they are attracted to each other, similar to the way the magnets stick together. This creates a compound called sodium chloride (NaCl), or table salt.
In conclusion, ionic bonding is the process where atoms with opposite charges stick together to create compounds like salt. It's like the way magnets stick together when opposite forces attract.
Related topics others have asked about:
