Isochoric process
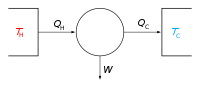
An isochoric process is when you have a very special kind of change that happens to some gas or liquid inside a container.
Imagine you have a balloon filled with air. Normally, you can squeeze the balloon to make the air inside take up less space. But in an isochoric process, you can't change how much space the air in the balloon takes up! That means you can't change the volume of the balloon. It has to stay the same size the whole time.
So how can you change the air inside the balloon without changing the volume? One way is to heat it up. When you heat a gas, its molecules move around faster and faster. As they move, they bump into each other and into the walls of the balloon. All these collisions cause the gas to push harder and harder against the walls of the balloon, increasing its pressure.
Another way to change the air inside the balloon without changing the volume is to cool it down. When you cool a gas, its molecules slow down and move less. As they bump into each other and into the walls of the balloon, they don't push as hard anymore. The pressure inside the balloon decreases as a result.
In an isochoric process, you can only change the pressure and temperature of the gas. The volume always stays the same. Scientists use isochoric processes to study how gases and liquids behave under different conditions. It helps them make predictions about how these fluids will behave in the real world.
Imagine you have a balloon filled with air. Normally, you can squeeze the balloon to make the air inside take up less space. But in an isochoric process, you can't change how much space the air in the balloon takes up! That means you can't change the volume of the balloon. It has to stay the same size the whole time.
So how can you change the air inside the balloon without changing the volume? One way is to heat it up. When you heat a gas, its molecules move around faster and faster. As they move, they bump into each other and into the walls of the balloon. All these collisions cause the gas to push harder and harder against the walls of the balloon, increasing its pressure.
Another way to change the air inside the balloon without changing the volume is to cool it down. When you cool a gas, its molecules slow down and move less. As they bump into each other and into the walls of the balloon, they don't push as hard anymore. The pressure inside the balloon decreases as a result.
In an isochoric process, you can only change the pressure and temperature of the gas. The volume always stays the same. Scientists use isochoric processes to study how gases and liquids behave under different conditions. It helps them make predictions about how these fluids will behave in the real world.
Related topics others have asked about:
