Isobaric process
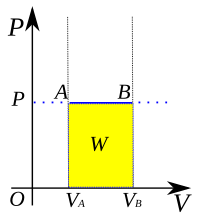
An isobaric process is when something stays at the same pressure while it is changing. So, let's imagine you have a balloon filled with air. You can squeeze the balloon to make it smaller and the air inside gets compressed. This means the air inside the balloon has changed, but the pressure it is trapped in hasn't changed - it's still the same as before you squeezed it. This type of change is called an isobaric process!
To give you another example, let's talk about cooking soup on the stove. When you heat up soup in a pot, the heat causes the water molecules in the soup to move faster, and this makes the soup hotter. This is still an isobaric process because the pressure in the pot stays the same, even though the temperature of the soup is changing.
Basically, with an isobaric process, you can think about something changing in some way, but the pressure it's at stays steady. It's like if you were trying to keep a toy from getting squished - if you put it in a box and applied pressure all around the box, it would keep the toy safe because the pressure is steady and not changing. That's what an isobaric process is!
To give you another example, let's talk about cooking soup on the stove. When you heat up soup in a pot, the heat causes the water molecules in the soup to move faster, and this makes the soup hotter. This is still an isobaric process because the pressure in the pot stays the same, even though the temperature of the soup is changing.
Basically, with an isobaric process, you can think about something changing in some way, but the pressure it's at stays steady. It's like if you were trying to keep a toy from getting squished - if you put it in a box and applied pressure all around the box, it would keep the toy safe because the pressure is steady and not changing. That's what an isobaric process is!
Related topics others have asked about:
