Yarkovsky effect
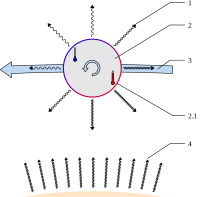
The Yarkovsky Effect is a force that affects the motion of an object in space. It is caused by the energy created when sunlight hits a space object and reflects off of it. Some of this energy is turned into heat, which means that the object will move slightly in the direction of the sunlight. This effect can be very small, but over time it can change the path of a space object. It is named after a scientist named Ivan Yarkovsky who discovered it in the early 1900s.
Related topics others have asked about:
