Biological neuron models
Imagine that your brain is like a big city full of busy roads where cars travel from one place to another. Neurons are like the cars that carry information through the roads of your brain.
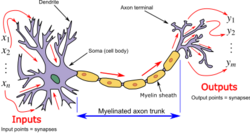
A biological neuron model is an attempt to create an artificial version of a real neuron. Think of it as a toy car that looks and behaves like a real car, but it's made of plastic and batteries instead of metal and gasoline.
In a real neuron, information travels through a series of tiny electrical and chemical processes. The neuron processes the information, decides what to do with it, and passes it on to other neurons. A biological neuron model tries to replicate this process using mathematical equations and computer simulations.
There are many different biological neuron models, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some models are better at simulating the behavior of real neurons, while others are better at processing large amounts of data quickly.
Overall, biological neuron models are an important tool for scientists studying the brain. By creating these models, researchers can better understand how the brain works, which can ultimately lead to improved treatments for neurological disorders and better artificial intelligence.
A biological neuron model is an attempt to create an artificial version of a real neuron. Think of it as a toy car that looks and behaves like a real car, but it's made of plastic and batteries instead of metal and gasoline.
In a real neuron, information travels through a series of tiny electrical and chemical processes. The neuron processes the information, decides what to do with it, and passes it on to other neurons. A biological neuron model tries to replicate this process using mathematical equations and computer simulations.
There are many different biological neuron models, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some models are better at simulating the behavior of real neurons, while others are better at processing large amounts of data quickly.
Overall, biological neuron models are an important tool for scientists studying the brain. By creating these models, researchers can better understand how the brain works, which can ultimately lead to improved treatments for neurological disorders and better artificial intelligence.
Related topics others have asked about:
