Boundary representation
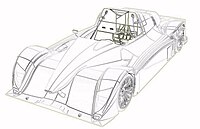
Boundary representation, also known as B-rep or boundary model, is a way to describe 3D shapes and objects by imagining them enclosed in a bubble or a shell.
Imagine a toy car that you can hold in your hand. On the outside, you can see the body of the car, with wheels, doors, windows, and other parts. But on the inside, there is empty space where the air flows through. Now, imagine that you can take the body of the car and turn it inside out, so that the empty space becomes the outside and the body becomes the inside. This is similar to the way B-rep works.
With B-rep, we describe the 3D objects using a combination of faces, edges, and vertices, just like we do with simple shapes like triangles or squares. These geometrical building blocks are used to create the shell that surrounds the object. Each face, edge, and vertex is assigned certain properties, such as location, size, shape, orientation, color, or texture.
For example, let's say we want to make a B-rep model of a ball. We start by creating a sphere shape, which is made up of faces, edges, and vertices. We then assign the properties of the sphere, such as its size and texture, to the faces, edges, and vertices. Next, we create a shell around the sphere by extruding the faces outwards. This creates an outer surface that describes the shape and boundaries of the ball.
Once we have the B-rep model of the ball, we can use it for various purposes, such as rendering, animation, simulation, or 3D printing. We can also manipulate the model by adding, subtracting, or modifying its faces, edges, or vertices. This allows us to create complex shapes and objects, such as buildings, machines, or human bodies.
Overall, B-rep is a powerful way to represent 3D shapes and objects that allows us to describe their boundaries and contents in a structured and organized way. It is used in many industries, such as manufacturing, product design, architecture, engineering, and entertainment.
Imagine a toy car that you can hold in your hand. On the outside, you can see the body of the car, with wheels, doors, windows, and other parts. But on the inside, there is empty space where the air flows through. Now, imagine that you can take the body of the car and turn it inside out, so that the empty space becomes the outside and the body becomes the inside. This is similar to the way B-rep works.
With B-rep, we describe the 3D objects using a combination of faces, edges, and vertices, just like we do with simple shapes like triangles or squares. These geometrical building blocks are used to create the shell that surrounds the object. Each face, edge, and vertex is assigned certain properties, such as location, size, shape, orientation, color, or texture.
For example, let's say we want to make a B-rep model of a ball. We start by creating a sphere shape, which is made up of faces, edges, and vertices. We then assign the properties of the sphere, such as its size and texture, to the faces, edges, and vertices. Next, we create a shell around the sphere by extruding the faces outwards. This creates an outer surface that describes the shape and boundaries of the ball.
Once we have the B-rep model of the ball, we can use it for various purposes, such as rendering, animation, simulation, or 3D printing. We can also manipulate the model by adding, subtracting, or modifying its faces, edges, or vertices. This allows us to create complex shapes and objects, such as buildings, machines, or human bodies.
Overall, B-rep is a powerful way to represent 3D shapes and objects that allows us to describe their boundaries and contents in a structured and organized way. It is used in many industries, such as manufacturing, product design, architecture, engineering, and entertainment.
Related topics others have asked about:
