Interquartile range
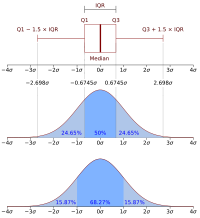
Interquartile range is a big word that helps us understand how spread out a bunch of numbers are. Imagine you have a big pile of candies that you want to share with your friends. You count how many candies you have, and write it down. Now you sort the candies from the smallest to the largest.
The interquartile range is the difference between the third quartile (75th percentile) and the first quartile (25th percentile) of your sorted candies. Let us say you have 20 candies, so you have five groups of candies, each consisting of 4 candies. The first group has 4 candies with the smallest values. The second group has 4 candies with slightly larger values than the first group, and so on until the last group.
Now let us assume that the first quartile is the 2nd group, meaning that 25% of the values in your candies fall in the 1st group, and 50% of values fall between the 2nd group and the 4th group. Assume that the third quartile is the 4th group, meaning that 75% of the values fall between your 2nd group of candies and the 4th group of candies.
So, the interquartile range is the difference between the highest value in your 4th group candies minus the smallest value in your 2nd group of candies. This shows us how spread out (or how similar) the values in your candies are. The larger the interquartile range, the more spread out the candies are, and the smaller the interquartile range, the more similar they are.
The interquartile range is the difference between the third quartile (75th percentile) and the first quartile (25th percentile) of your sorted candies. Let us say you have 20 candies, so you have five groups of candies, each consisting of 4 candies. The first group has 4 candies with the smallest values. The second group has 4 candies with slightly larger values than the first group, and so on until the last group.
Now let us assume that the first quartile is the 2nd group, meaning that 25% of the values in your candies fall in the 1st group, and 50% of values fall between the 2nd group and the 4th group. Assume that the third quartile is the 4th group, meaning that 75% of the values fall between your 2nd group of candies and the 4th group of candies.
So, the interquartile range is the difference between the highest value in your 4th group candies minus the smallest value in your 2nd group of candies. This shows us how spread out (or how similar) the values in your candies are. The larger the interquartile range, the more spread out the candies are, and the smaller the interquartile range, the more similar they are.
Related topics others have asked about:
