Optical activity
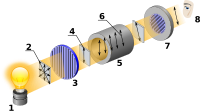
Optical activity is a fancy term for something that happens when light goes through certain substances. Imagine you have a bowl of juice with some sugar in it. When you stir the sugar in the juice, it makes the juice sweeter. Well, some substances can "stir" light as it passes through them, making the light bend in different ways. This is called optical activity.
The substances that can do this are called chiral molecules. They have a special shape that is like a mirror image of itself. Imagine if you had a right hand and a left hand that looked the same, but one was flipped over like a mirror image. That's kind of what chiral molecules are like.
When light passes through a chiral molecule, it interacts with the shape and gets "twisted" in a certain way. This can change the direction that the light is going or change how much light gets through. It's like putting on a pair of tinted glasses - the light looks a little different.
Scientists use optical activity to study chiral molecules and learn more about their properties. Optical activity also has practical uses in real life, such as in medicine. For example, certain drugs or vitamins may be chiral molecules and their optical activity can affect how they are absorbed in the body. Understanding this can help doctors choose the right medicine for their patients.
The substances that can do this are called chiral molecules. They have a special shape that is like a mirror image of itself. Imagine if you had a right hand and a left hand that looked the same, but one was flipped over like a mirror image. That's kind of what chiral molecules are like.
When light passes through a chiral molecule, it interacts with the shape and gets "twisted" in a certain way. This can change the direction that the light is going or change how much light gets through. It's like putting on a pair of tinted glasses - the light looks a little different.
Scientists use optical activity to study chiral molecules and learn more about their properties. Optical activity also has practical uses in real life, such as in medicine. For example, certain drugs or vitamins may be chiral molecules and their optical activity can affect how they are absorbed in the body. Understanding this can help doctors choose the right medicine for their patients.
Related topics others have asked about:
