Radioisotope heater units
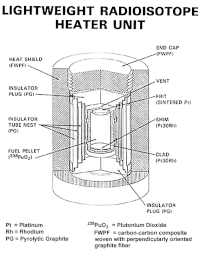
Radioisotope heater units are small devices that produce heat using a special material called a radioisotope. A radioisotope is a type of atom that emits energy in the form of radiation. This energy can be used to generate heat, and that's what radioisotope heater units do.
The radioisotope used in these units is usually plutonium-238. This material is very useful because it produces a lot of heat and has a very long half-life, which means it will continue to produce heat for a long time. However, plutonium-238 is also dangerous and can be toxic, so it's important to handle it carefully.
Radioisotope heater units are used in a variety of applications, including space exploration. When spacecraft travel far from the sun, they can get very cold. If the equipment on board gets too cold, it may malfunction or stop working altogether. Radioisotope heater units provide a constant source of heat to keep the equipment operating normally.
These units are also used in scientific experiments that require a stable source of heat, such as testing the properties of certain materials or studying the behavior of organisms in extreme temperatures.
Overall, radioisotope heater units are small but powerful devices that provide heat using a special type of atom. They are used in many different applications, including space exploration and scientific research.
The radioisotope used in these units is usually plutonium-238. This material is very useful because it produces a lot of heat and has a very long half-life, which means it will continue to produce heat for a long time. However, plutonium-238 is also dangerous and can be toxic, so it's important to handle it carefully.
Radioisotope heater units are used in a variety of applications, including space exploration. When spacecraft travel far from the sun, they can get very cold. If the equipment on board gets too cold, it may malfunction or stop working altogether. Radioisotope heater units provide a constant source of heat to keep the equipment operating normally.
These units are also used in scientific experiments that require a stable source of heat, such as testing the properties of certain materials or studying the behavior of organisms in extreme temperatures.
Overall, radioisotope heater units are small but powerful devices that provide heat using a special type of atom. They are used in many different applications, including space exploration and scientific research.
Related topics others have asked about:
