Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
Imagine you want to send a message to your friend, who is far away from you. You can use a special device called a laser, which shoots out a narrow beam of light. This beam of light can travel over long distances and can carry your message.
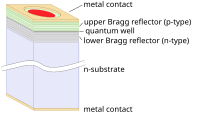
Now, a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser, or VCSEL for short, is a special type of laser that is made to work better than regular lasers. The way it works is like this: picture a small flat disc, like a tiny pancake, with two layers inside. One of these layers is a material that can soak up light energy, while the other is a material that can release light energy. In between these two layers, there is a special cavity, kind of like a tiny hole where the light can escape.
When you give energy to the first layer by passing some electricity through it, it gets excited and starts to release light energy. This light then bounces back and forth between the two layers, getting stronger and stronger in the cavity. Eventually, the light becomes so powerful that it shoots out of the cavity in a beam of light. The light beam then travels through the air and can be used to send messages just like any other laser.
So, why is a VCSEL better than a regular laser? Well, there are a few reasons. First, VCSELs can be made very small, so they can fit into tiny electronic devices, like smartphones and laptops! Also, they use less energy than regular lasers, which means they don't drain batteries as quickly. Finally, because the laser beam comes out straight up from the surface of the disc, it's easier to aim and use for things like 3D imaging or facial recognition.
Overall, a VCSEL is a really cool little device that helps us send messages quickly and accurately across long distances.
Now, a vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser, or VCSEL for short, is a special type of laser that is made to work better than regular lasers. The way it works is like this: picture a small flat disc, like a tiny pancake, with two layers inside. One of these layers is a material that can soak up light energy, while the other is a material that can release light energy. In between these two layers, there is a special cavity, kind of like a tiny hole where the light can escape.
When you give energy to the first layer by passing some electricity through it, it gets excited and starts to release light energy. This light then bounces back and forth between the two layers, getting stronger and stronger in the cavity. Eventually, the light becomes so powerful that it shoots out of the cavity in a beam of light. The light beam then travels through the air and can be used to send messages just like any other laser.
So, why is a VCSEL better than a regular laser? Well, there are a few reasons. First, VCSELs can be made very small, so they can fit into tiny electronic devices, like smartphones and laptops! Also, they use less energy than regular lasers, which means they don't drain batteries as quickly. Finally, because the laser beam comes out straight up from the surface of the disc, it's easier to aim and use for things like 3D imaging or facial recognition.
Overall, a VCSEL is a really cool little device that helps us send messages quickly and accurately across long distances.
Related topics others have asked about:
