Chemiosmotic potential
Okay, kiddo, let's learn about chemiosmotic potential! First, we need to know that all living things need energy to survive. We get that energy from the food we eat, right? But, did you know that our cells also need energy to work properly and stay alive? That energy comes from a tiny but very important part of our cells called mitochondria.
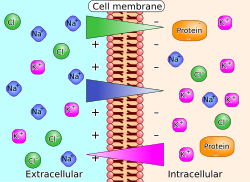
Mitochondria are like little powerhouses that make energy for our cells. They do it using a special process called respiration which involves breaking down glucose (or sugar) molecules. This process happens in a series of steps that release energy bit by bit. One important step is where electrons (tiny negatively charged particles) are passed through different molecules that are embedded in the mitochondria's membrane.
Now, here's where it gets a little bit tricky. When electrons move through those molecules, they create a difference in charge between the inside and the outside of the membrane. This difference is like a battery waiting to be used. And, that's where the chemiosmotic potential comes in!
The chemiosmotic potential is the ability of this charge difference to do work. It's like a force that can move things. It's called "chemio" because it's involved in chemical reactions and "osmotic" because it has to do with water movement.
The mitochondria use this potential to create ATP, which is a molecule that stores energy. ATP is like a tiny battery that our cells can use whenever they need energy. To make ATP, the mitochondria use a special enzyme called ATP synthase to channel the charged particles through the membrane. This enzyme acts like a turbine, spinning around as the charged particles pass through it. The energy from the spinning turbine helps make ATP molecules.
So, there you have it! The chemiosmotic potential is like a battery that helps our mitochondria make energy for our cells. And, our cells use that energy to do all sorts of important things like moving, growing, and repairing themselves.
Mitochondria are like little powerhouses that make energy for our cells. They do it using a special process called respiration which involves breaking down glucose (or sugar) molecules. This process happens in a series of steps that release energy bit by bit. One important step is where electrons (tiny negatively charged particles) are passed through different molecules that are embedded in the mitochondria's membrane.
Now, here's where it gets a little bit tricky. When electrons move through those molecules, they create a difference in charge between the inside and the outside of the membrane. This difference is like a battery waiting to be used. And, that's where the chemiosmotic potential comes in!
The chemiosmotic potential is the ability of this charge difference to do work. It's like a force that can move things. It's called "chemio" because it's involved in chemical reactions and "osmotic" because it has to do with water movement.
The mitochondria use this potential to create ATP, which is a molecule that stores energy. ATP is like a tiny battery that our cells can use whenever they need energy. To make ATP, the mitochondria use a special enzyme called ATP synthase to channel the charged particles through the membrane. This enzyme acts like a turbine, spinning around as the charged particles pass through it. The energy from the spinning turbine helps make ATP molecules.
So, there you have it! The chemiosmotic potential is like a battery that helps our mitochondria make energy for our cells. And, our cells use that energy to do all sorts of important things like moving, growing, and repairing themselves.
Related topics others have asked about:
