Colour temperature
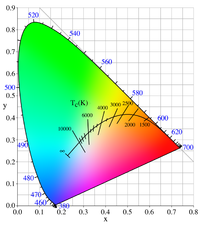
Colour temperature is a way of describing the colour of light that we see. Just like how some things seem more white, yellow, or blue in different kinds of light, so does light itself have different colours. Scientists have come up with a way of measuring these colours using something called Kelvin degrees.
When we think of temperature, we usually think of hot and cold. In the same way, colour temperature is measured on a scale from warm to cool. Warm colours (like the orangey-yellow glow from a fireplace) have lower Kelvin values and cool colours (like the blueish-white light from a computer screen) have higher Kelvin values.
Basically, the lower the Kelvin value, the redder/oranger the light will appear, and the higher the Kelvin value, the bluer/whiter the light will appear. For example, sunlight has a colour temperature of around 5500K and is considered a “cool” white, while an incandescent bulb emits light at around 2700K and is considered a “warm” yellow-orange colour.
Knowing about colour temperature is important because it can affect how colours look. If you've ever taken a photo under fluorescent lighting and noticed it looked really yellow, that's because the bulbs have a different colour temperature than natural light. The same goes for choosing light bulbs for your home - you might want a “warm” colour temperature for a cozy atmosphere in the bedroom, but a “cool” temperature for a bright workspace.
When we think of temperature, we usually think of hot and cold. In the same way, colour temperature is measured on a scale from warm to cool. Warm colours (like the orangey-yellow glow from a fireplace) have lower Kelvin values and cool colours (like the blueish-white light from a computer screen) have higher Kelvin values.
Basically, the lower the Kelvin value, the redder/oranger the light will appear, and the higher the Kelvin value, the bluer/whiter the light will appear. For example, sunlight has a colour temperature of around 5500K and is considered a “cool” white, while an incandescent bulb emits light at around 2700K and is considered a “warm” yellow-orange colour.
Knowing about colour temperature is important because it can affect how colours look. If you've ever taken a photo under fluorescent lighting and noticed it looked really yellow, that's because the bulbs have a different colour temperature than natural light. The same goes for choosing light bulbs for your home - you might want a “warm” colour temperature for a cozy atmosphere in the bedroom, but a “cool” temperature for a bright workspace.
Related topics others have asked about:
